Introduction and Learning Objectives | Climate change: What is it and how did we get there? |Climate action: How can you support it? | Climate denialism terminology | What is climate denialism?| Who are climate deniers? | The causes of climate denialism | Climate denialism: The role of social media | Final quiz | Europass
This lesson explores the concept of climate denialism, its causes, and its effects on public discourse and policy. Throughout the lesson, you will explore what climate denialism is, develop an understanding of its causes, and learn how to counter climate denialism.
Lesson duration
You can complete this lesson at your own pace. It is possible to complete the lesson in one sitting or on several occasions. The entire lesson takes approximately 2 hours.
Learning Objectives
By the end of this lesson, you will be able to:
1. Understand the concept of climate denialism, as well as the causes, effects and consequences.
2. Understand how to use information online in an ethical way following netiquette.
3. Explore and understand the concept of climate change, as well as the cause behind it and its historical development over time.
4. Understand and apply strategies for climate behaviour and learn how to contribute to climate action
Climate change: What is it and how did we get here?
Climate denialism describes an attitude that refuses to acknowledge human-made climate change and its effects and/or the effectiveness of strategies to counter climate change.
As a first step to understanding climate denialism, it is important to understand climate change. What is climate change? How are humans impacting the climate? What are the effects of climate change, and what can we do about it? The answers to these questions will then help you to understand climate denialism.
Take a look at the presentation below for a quick recap of what climate change is. If you would like to learn more about climate change and its causes, head over to Lesson 2: Climate Change.
Take a moment to familiarise yourself with the terms below or to refresh your memory on what they mean. You can return to this list at any point throughout the course if you encounter a term that you do not know the meaning of.
Climate action: How can you support it?
From the presence of climate change and the question of how it came about, follows the question: What can we do about it? Likewise, climate denialism is not only connected to climate change itself, but to climate action as well. It is therefore worth taking a closer look at what we – as individuals can do to counter climate change.
While individual action alone will not stop climate change, it is nonetheless effective in contributing to climate action. According to the UN, if one billion individuals (of a global population of 8.025 billion people in 2023) took practical steps to reduce their impact on the planet, it would be possible to reduce global carbon emissions by up to 20% (UNEP, 2020). Here are some ideas on how you can reduce your carbon footprint and thereby contribute to climate action.
Take a look at the illustrations below to see what individuals can do to support climate action and changes within politics, economy and society.
🚲 Cycle or walk instead of driving.
🚙 If you need a car, choose electric.
🚉 Avoid travelling by plane.

🥦 Eat more plant-based food.
👩🌾 Buy seasonal, organic, and locally grown produce.
🛒 Reduce waste, i.e., by meal planning, buying only what you need, and shopping plastic-free.
🧣 Buy i.e., clothes and furniture second-hand.
🧵 Repair and reuse instead of throwing away.
⚡ Reduce your energy consumption: Switch off lights and unplug electric devices when you don’t need them.
☀️ Switch to renewable energies: Check for options with your energy provider. Install solar panels if you have the option.

💬 Talk to your local political representative.
💡 Speak to other people to raise awareness and exchange ideas.
💪 Participate in initiatives such as local park or beach clean-ups.

Now that you know how individuals can reduce their impact on the planet and, in this way, contribute to climate action, reflect on the following questions:
- Which of these actions do you take already?
- Which ones are you able to implement in your life?
- Are there any other ways in which you could contribute to climate action?
Climate denialism terminology
Climate denialism sounds like an easy enough concept: The denial of climate change. But at a closer look it is more complex than we might think at first. Equipped with knowledge about climate change and climate action as well as the relevant terminology, you are now prepared to explore climate denialism and the different forms it takes; from the denial of the existence of climate change to scepticism about whether climate action really makes a difference.
Take a look at the list of terms below. Familiarise yourself with the concepts that are unfamiliar to you. If you encounter a term throughout the course that you do not understand you can always return to this list.
What is climate denialism?
Now, that you are familiar with the most important climate denialism terms, let’s dive into what exactly climate denialism is.
In today’s era, when we search for ‘Climate change’ on search engines, two phrases that surface immediately are “climate change denialism” and “climate change deniers.” However, what precisely do these phrases signify, and why are they frequently sought after?
Over the past few decades, climate change and ways to address its effects have become a major topic of discussion. At the same time, some people challenge the idea that climate change is real or caused by human activity, even though there is strong evidence to prove it. This way of thinking is called denial.
Although we can see clear signs of climate change in our daily lives, like rising temperatures in cities, some people still refuse to accept it as a fact. People who deny climate change might argue that it’s just a natural process that has always happened and some also believe that human actions have little impact on the environment. This way of thinking, called “magical thinking,” is based on the belief that thoughts or actions can change reality, allowing people to avoid facing an uncomfortable truth about the climate crisis.
Now that you have a general idea of what climate denialism is – essentially the refusal to accept the reality of climate change despite scientific evidence – let’s take a look at how debates on and awareness of climate changed has changed over time. Being familiar with common perspectives on climate change, will help you recognise specific arguments and assess whether they are based on scientific fact or misinformation.

In the next step, you will deepen your understanding of the different forms of climate denialism by looking at different climate denier profiles.
Who are climate deniers?
Not every person who denies climate change has the same reasons, viewpoints and arguments. Through this activity, you will become familiar with different profiles of climate deniers. Understanding the different points of view will help you identify climate denialism when you encounter it in everyday life, and as a next step, work against it.
Take a look at the presentation below to learn about the different denial profiles.
The causes of climate denialism
To go beyond recognising climate denialism when we encounter it, and work against it, it is important to understand where it comes from. In this activity, you will explore the educational, economic, political, and cultural root causes of climate denialism.
Take a look at the presentation below to learn about the educational, economic, political, and cultural reasons that lead to climate denialism.
Climate denialism: The role of social media
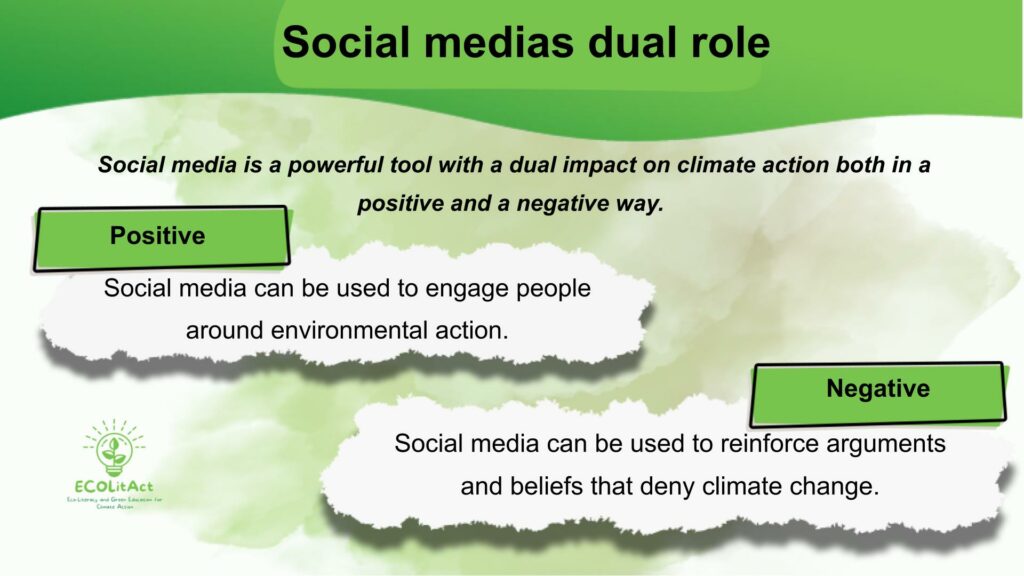
We live in a digital age, so naturally climate denialism emerges online as well as offline. Especially social media play a role in the spreading of mis- and disinformation on climate change and shaping public perceptions of climate change. After completing this activity, you will know the difference between mis- and disinformation and will be able to identify them online. You will have gained understanding of the role of social media as well as skills to counteract climate denialism online.

The difference between mis-and disinformation
Misinformation is the unintentional spread of false information due to misconceptions or lack of knowledge, whereas disinformation is the intentional dissemination of misleading information with the intent to deceive, often to protect certain interests and maintain the status quo. Identifying these differences can help people better evaluate the information they encounter.
Both mis-and disinformation harm the environment by fueling climate denialism, especially on social media, which exploits users’ fears and vulnerabilities, such as a lack of climate literacy and critical thinking skills. This has resulted in widespread public misperceptions about climate change and has shaped the public discourse surrounding the issue.
Many industries, particularly the fossil fuel industry, are often responsible for disinformation which has the intention to spread false information, and often conceived by conservative think tanks and front groups. The strategy here is to create doubt, encourage disagreement and foster division. Research has shown that this strategy works, as it can contribute to political inaction and even to the rejection of mitigation policies.
Combating mis- and disinformation
Similar to offline spaces, people interact with each other on social media and other online spaces. And just as is the case online, there are certain norms and behaviours that should be followed. By sticking to this netiquette you contribute to creating safe spaces online and avoid spreading false information yourself.
Take a look at the infographic below to find out more.

Are there any other aspects that you think are – or should be – important online?
If you would like to learn more about this, we recommend that you take Lesson 1: Tackling Misinformation and Media and Information Literacy (MIL)
Now that you know what role social media plays and how to act online, take a look at the infographic below to find out how to actively combat mis- and disinformation online.


Final quiz
We are almost at the end of this lesson and now it is time for you to apply your knowledge on climate denialism and your critical thinking skills in the following quiz. Match each response with a statement at the bottom.
Good job!
You’re now finished with the Explorer level lesson on climate denialism!
If you would like to learn more about climate denialism and how to combat it, you can continue with the Practitioner Level lesson on climate denialism.
Showcase your new skills with Europass
You have just completed another step in your learning journey. The skills and knowledge you have gained are valuable – not just for countering climate denialism and contributing to a greener future, but also for opening doors to new opportunities for you! A great way to do this is by adding them to your Europass profile.
Europass is a European Union initiative that helps individuals communicate their skills, qualifications, and experiences clearly and effectively. It consists of several documents, including the Europass CV, which is recognised across Europe and beyond, making it easier for learners to present their qualifications to potential employers or educational institutions.
If you don’t yet have a Europass profile, creating one takes just a few minutes. Get started here. And if you need a little help to set things up, you can take a look at this video tutorial.
For the lesson you have just completed, we encourage you to add the following skills:
- In-depth understanding of climate denialism, its causes, and its societal impact
- Identification and analysis of climate denialism narratives and viewpoints
- Recognition of behaviours contributing to climate denialism in various contexts
- Knowledge of factors behind climate denialism
- Assessment of misinformation’s role in reinforcing climate denialism
- Development of strategies and initiatives to counteract climate denialism
